|
ZINC GLUCONATE
| ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 4468-02-4 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 224-736-9 | |
| FORMULA | C12H22O14Zn.3H2O | |
| MOL WT. | 455.68 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2918.16 |
|
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: > 5,000 mg/kg |
|
| SYNONYMS | Gluconato de Zinc; 葡萄糖酸锌; | |
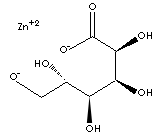
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
GLUCONATES / | |
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to off-white powder or granules | |
| MELTING POINT | ||
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
| |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | 100 g/l | |
| pH |
5.5 - 7.5 (1% Sol.) | |
| VAPOR DENSITY |
| |
| AUTOIGNITION |
| |
| NFPA RATINGS | ||
| REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT |
| |
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Zinc is an essential mineral having a role in the maintenance of the body's nervous and immune systems (T-cell function). This mineral is involved in the biochemical reactions as an antioxidant in the healing process and develops normal tissues Zinc is a cofactor in enzymatic reactions such as protein synthesis polymerases and in carbonic acid anhydrase. Zinc maintains the body's alkaline balance. Zinc finger, a structural domain found in many gene-regulatory proteins, is a component of hydrophobic hormones acting stabilizing the biomembrane structures and cell membrane metabolism. Zinc deficiencies may result in prolonged wound healing, delayed sexual maturation, mental lethargy, skin changes, and susceptibility to infections. Gluconate and citrate forms are mainly used as zinc supplements. They are easily absorbed by the body. Zinc Gluconate can be formulated in pharmaceuticals, and foods as a zinc supplement. Zinc Gluconate is used as an ingredient to treat common cold and various hygienic products. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
USP |
||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white powder or granules | |
| IDENTIFICATION |
pass (Test A, Test B) |
|
|
ASSAY |
98.0 - 102.0% (Anhydrous Basis) |
|
|
ZINC CONTENT |
13.9 - 14.6 % | |
|
CHLORIDE |
0.05% max |
|
|
SULFATE |
0.05% max |
|
|
ARSENIC |
3ppm max |
|
|
CADMIUM |
5ppm max |
|
|
LEAD |
10ppm max |
|
|
WATER |
11.6% max |
|
|
REDUCING MATTERS |
1.0% max |
|
|
pH |
5.5 - 7.5 (1% Sol.) |
|
|
OVI |
pass test (Organic Volatile Impurities) |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 50kgs
in fiber drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
|
Gluconic acid is a polyhydroxycarboxylic acid
with six carbon length. It is derived from glucose by
oxidation of the aldehyde group on the C-1 to a carboxyl group. It is abundant
in plants, fruits and other foodstuffs. Commercially the physiological d-form
gluconic acid is prepared by fermentation process. It has a carboxylic group and
five hydroxy groups, and thus is a good chelator particularly in alkaline
conditions. Chelation is a chemical combination with a metal in complexes in
which the metal is part of a ring. Organic ligand is called chelator or
chelating agent, the chelate is a metal complex. The larger number of ring
closures to a metal atom is the more stable the compound. Chelation is applied
in metal complex chemistry, organic and inorganic chemistry, biochemistry, and
environment protection. It is used in chemotherapeutic treatments for metal
poisoning. Chelating agents offers a wide range of sequestrants to control metal
ions in aqueous systems. By forming stable water soluble complexes with
multivalent metal ions, chelating agents prevent undesired interaction by
blocking normal reactivity of metal ions. Heavy metals are chelated in alkaline
solution and their interferences are eliminated gluconic acid. Concentrated
gluconic acid solution contains certain lactone structure, a neutral cyclic
ester, showing antiseptic property. Gluconic acid and its derivatives (salts or
esters) are used in the formulation of pharmaceuticals, foods, and cosmetics as
mineral supplements to prevent the deficiency and as buffer salts. They are used
as ingredients in various hygienic products. In industrial applications, they
are used for scale removal in metal cleanings, industrial and household cleaning
compounds including mouth washer, metal finishing, water treatments, and as
paper and textile auxiliaries.
|
||